The Heart of the Soul Nebula
Image Credit & Copyright: Nicola Bugin
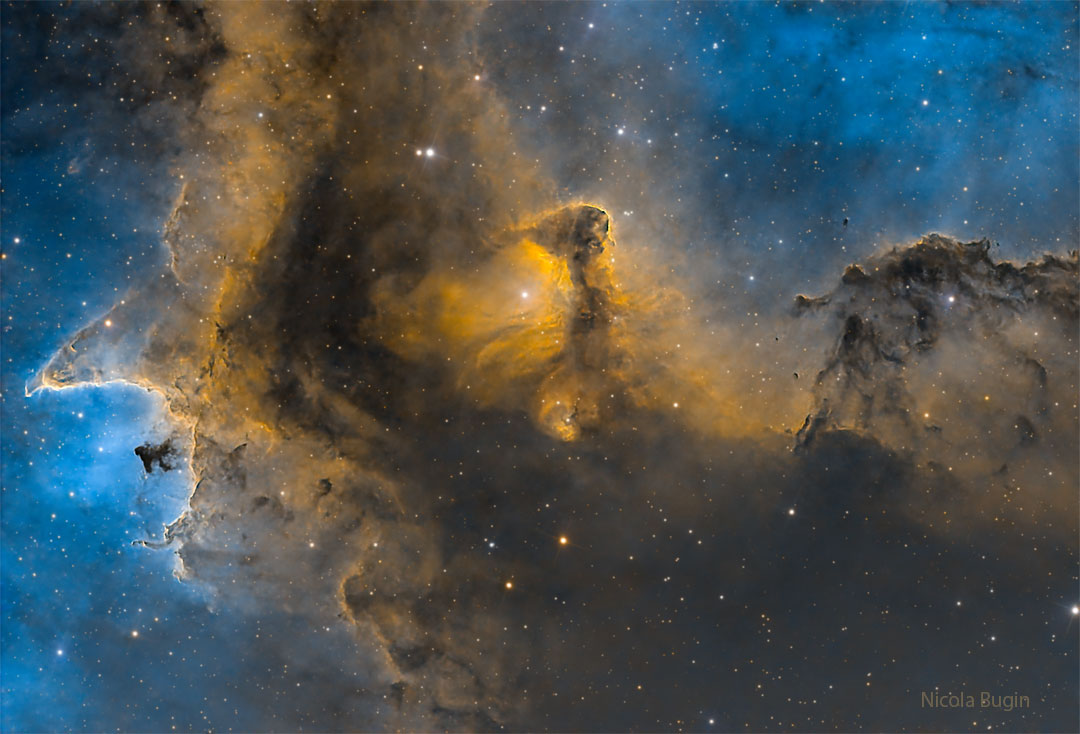
Explanation: This cosmic close-up looks deep inside the Soul Nebula. The dark and brooding dust clouds outlined by bright ridges of glowing gas are cataloged as IC 1871. About 25 light-years across, the telescopic field of view spans only a small part of the much larger Heart and Soul nebulae. At an estimated distance of 6,500 light-years, the star-forming complex lies within the Perseus spiral arm of the Milky Way, seen in planet Earth’s skies toward the constellation of the Queen of Aethiopia (Cassiopeia). An example of triggered star formation, the dense star-forming clouds of IC 1871 are themselves sculpted by the intense winds and radiation of the region’s massive young stars. This color image adopts a palette made popular in Hubble images of star-forming regions.
Tomorrow’s picture: open space